Direct Sales vs Indirect Sales: What's the Difference?
In the world of business, sales play a crucial role in driving revenue and growth. However, not all sales approaches are created equal. Direct sales and indirect sales are two distinct strategies that companies employ to reach their target markets. Understanding the difference between these approaches is essential for any business looking to optimize its sales efforts. In this article, we will delve into the definitions, differences, and examples of both direct sales and indirect sales
Defining Direct Sales and Indirect Sales
When it comes to selling products or services, there are two primary approaches: direct sales and indirect sales. Each method has its own unique characteristics and benefits. Let's take a closer look at what direct sales and indirect sales entail.
1.1 - What is Direct Sales?

Direct sales involve selling products or services directly to the end consumer without intermediaries. In this approach, companies typically rely on their own salesforce to connect with customers and close deals. Direct sales can take various forms, including in-person meetings, phone calls, or online interactions.
One key characteristic of direct sales is the direct relationship between the seller and the buyer. This direct connection allows for personalized communication and a tailored sales experience. When engaging in direct sales, companies have the opportunity to build strong relationships with their customers, understanding their needs and preferences on a deeper level.
Moreover, direct sales often require extensive product knowledge and strong interpersonal skills to effectively engage customers and persuade them to make a purchase. Sales representatives need to be well-versed in the features and benefits of the products or services they are selling, as well as possess the ability to address any concerns or objections the customers may have.
Furthermore, direct sales can offer a higher level of control for companies. By managing the entire sales process internally, businesses have the ability to maintain consistent messaging, pricing, and customer experience. This control can be particularly advantageous for companies with complex or customizable products, as it allows for a more hands-on approach to sales.
1.2 - What is Indirect Sales?
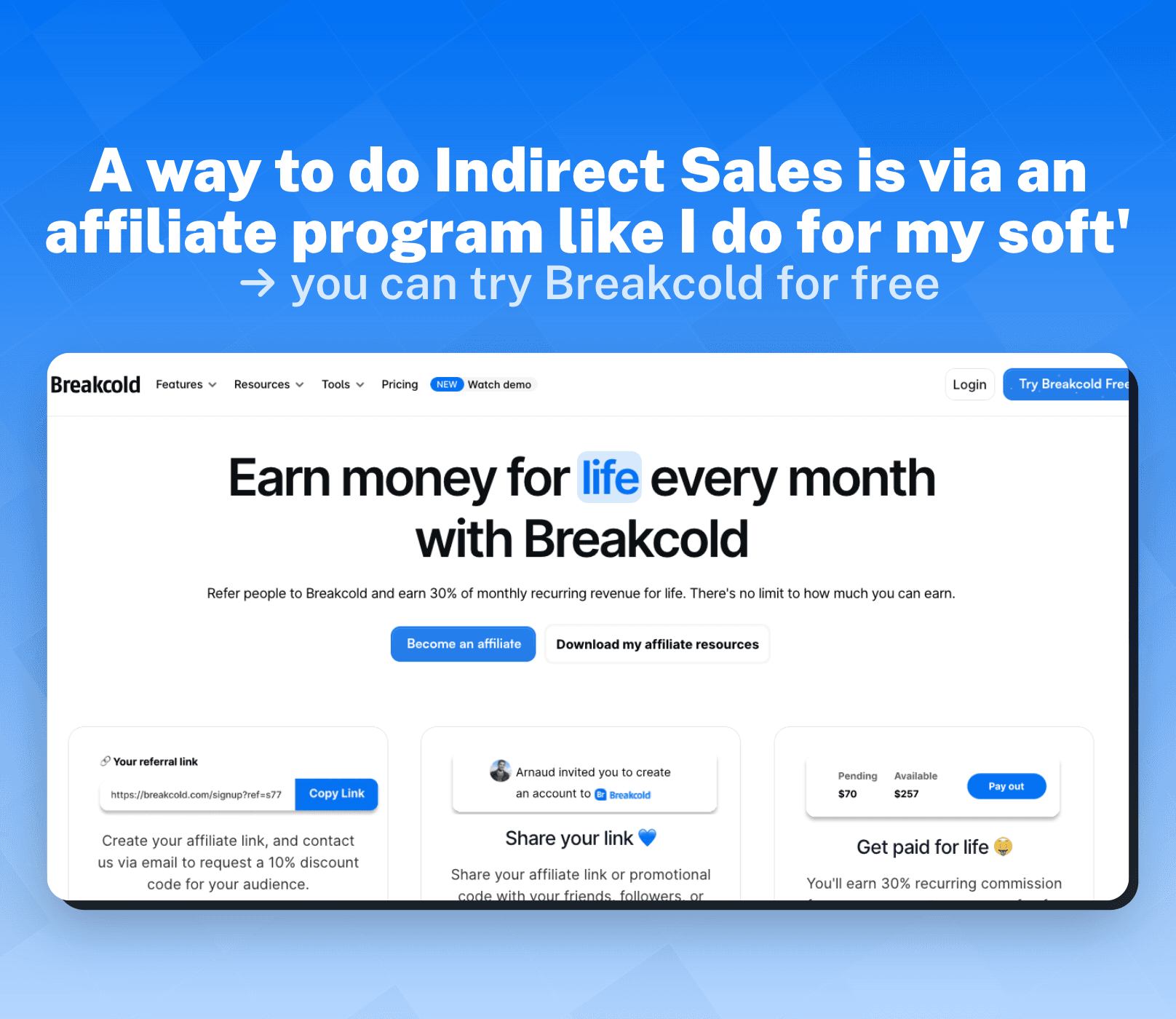
In contrast to direct sales, indirect sales involve selling products or services through intermediaries. These intermediaries can be resellers, distributors, or even affiliates. In this sales model, companies rely on third-party channels to reach the end consumer.
Indirect sales can take various forms, such as selling through retail stores, partnering with online marketplaces, or utilizing independent sales representatives. With indirect sales, the company's salesforce works indirectly by leveraging the resources and reach of the intermediaries. This approach allows businesses to tap into existing distribution networks, benefit from established relationships, and expand their market presence without directly managing every customer interaction.
One of the key advantages of indirect sales is the ability to reach a wider audience. By partnering with established distributors or retailers, companies can access customers who may not have been aware of their products or services otherwise. This broader reach can lead to increased brand exposure and potential sales opportunities.
Additionally, indirect sales can provide companies with cost savings and efficiencies. By leveraging the infrastructure and expertise of intermediaries, businesses can reduce the need for extensive salesforce training and management. Instead, they can focus on developing strong partnerships and supporting their distribution channels.
Furthermore, indirect sales can be particularly beneficial for companies entering new markets or industries. By collaborating with local distributors or resellers, businesses can leverage their knowledge of the market and existing customer relationships. This can help overcome barriers to entry and accelerate market penetration.
It's important to note that while indirect sales offer many advantages, they also come with their own set of challenges. Companies must carefully select and manage their intermediaries to ensure brand consistency, pricing integrity, and customer satisfaction. Effective communication and collaboration between the company and its intermediaries are crucial for success in indirect sales.
In conclusion, both direct sales and indirect sales have their own merits and can be effective strategies for businesses depending on their goals, target market, and resources. Whether it's building personal relationships through direct sales or leveraging distribution networks in indirect sales, companies have the opportunity to connect with customers and drive revenue in various ways.
What's the Difference between Direct Sales and Indirect Sales?
Now that we have defined direct sales and indirect sales, let's explore the key differences between these two approaches.
Level of Control: In direct sales, companies have full control over the sales process, customer interactions, and sales outcomes. They directly manage their salesforce and have a deep understanding of customer needs. In contrast, indirect sales involve relinquishing a certain degree of control to intermediaries. Companies must trust the capabilities and commitment of their partners to effectively sell their products or services.
Customer Relationship: Direct sales foster a direct relationship between the company and the customer. This close connection enables personalized communication, relationship building, and a better understanding of customers' evolving needs. Indirect sales, on the other hand, rely on the intermediaries to maintain relationships with the end consumer. While indirect sales may sacrifice a bit of intimacy, they can leverage the intermediaries' expertise and established trust to reach a wider customer base.
Profit Margin: Direct sales often command higher profit margins due to the absence of intermediaries. By selling directly, companies eliminate the margin that would otherwise be shared with resellers or distributors. Indirect sales, although involving a revenue-sharing model with intermediaries, can enable businesses to access a larger customer pool and drive higher sales volumes.
Examples of the Difference between Direct Sales and Indirect Sales
2.1 - Example in a Startup Context
Consider a startup that has developed a cutting-edge software product. If the startup employs direct sales, its sales team will personally engage with potential customers through demos, presentations, and negotiation meetings. The sales team will have a deep understanding of the software's capabilities and be able to address specific customer pain points. In contrast, if the startup adopts an indirect sales approach, it may partner with established software distributors who already have access to a vast customer base. The distributors will handle the actual sales process while the startup focuses on product development and strategic partnerships.
2.2 - Example in a Consulting Context
In a consulting business, a direct sales approach may involve consultants reaching out to potential clients directly, assessing their needs, and proposing tailored solutions. The consultants build strong relationships with clients and provide ongoing support throughout the engagement. On the other hand, an indirect sales approach could involve partnering with other consulting firms or industry associations to offer bundled services. This collaboration allows the consulting firm to access a broader market and tap into the established reputation and client base of its partners.
2.3 - Example in a Digital Marketing Agency Context
Digital marketing agencies can employ both direct and indirect sales strategies. Direct sales may involve the agency's sales team reaching out to businesses directly, showcasing their expertise in online advertising, SEO, or social media marketing. The agency can highlight its track record and success stories to win clients. In contrast, indirect sales for a digital marketing agency could come through partnerships with web development companies or graphic design agencies. The agency's services can be offered as value-add options to complement the partners' core offerings, creating a win-win situation for both parties.
2.4 - Example with Analogies
To illustrate the difference between direct and indirect sales, let's consider two scenarios. In direct sales, imagine you are buying a car directly from the manufacturer. You have the opportunity to test drive the vehicle, negotiate the price, and discuss customization options with the salesperson. On the other hand, indirect sales would be akin to purchasing the car through a dealership. The dealership serves as the intermediary, showcasing the car, handling the paperwork, and providing after-sales service. While you may not interact with the manufacturer directly, the dealership creates a convenient and trusted buying experience.
In Conclusion
Direct sales and indirect sales are two distinct approaches businesses can take to reach their target markets. Direct sales involve selling directly to customers without intermediaries, allowing for personalized interactions and higher profit margins. On the other hand, indirect sales leverage intermediaries to reach a broader customer base and tap into established distribution networks. Understanding the differences between these approaches and their suitability for different contexts is crucial for businesses looking to optimize their sales strategies and drive revenue growth.