Conversion Funnel vs. Conversion Path: What's the Difference?
In the ever-evolving world of digital marketing, it's crucial to have a solid understanding of key concepts and terminology. Two commonly used terms that often cause confusion are "conversion funnel" and "conversion path." While these terms may sound similar, they refer to distinct aspects of the customer journey. In this article, we will define and explore the difference between a conversion funnel and a conversion path, providing examples to clarify their distinctions
Defining Conversion Funnel and Conversion Path
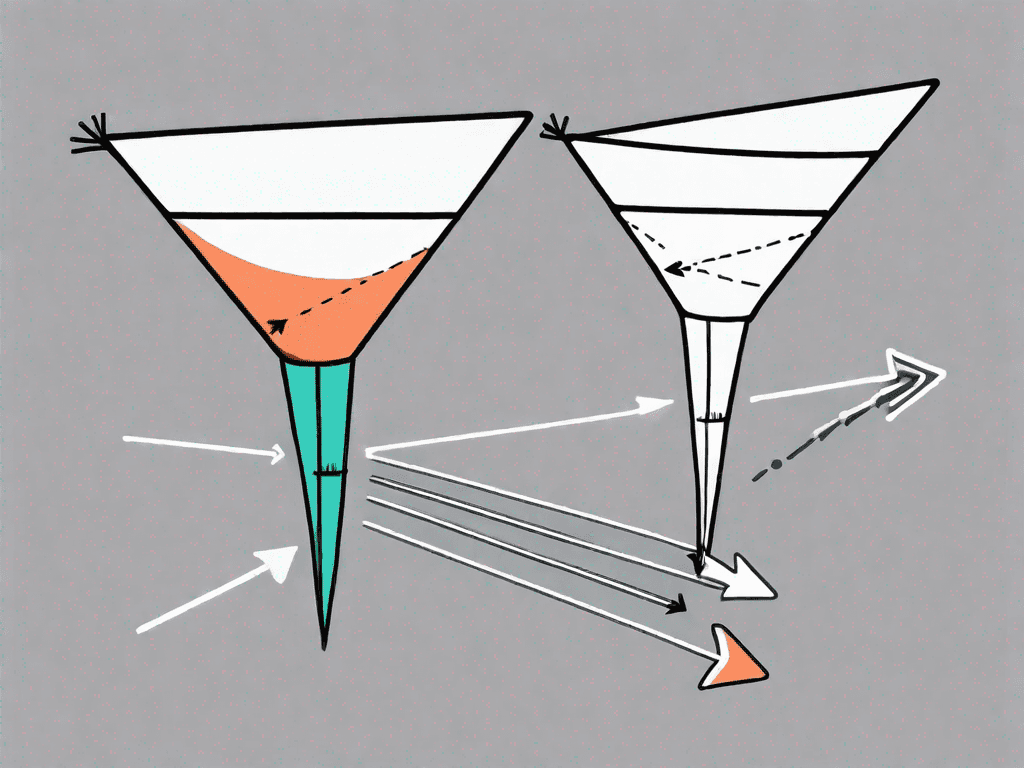
A conversion funnel is a visual representation of the stages a potential customer passes through from initial exposure to making a purchase or completing a desired action. It resembles a funnel because it narrows down the number of people who progress through each stage, eventually leading to conversions. The classic stages of a conversion funnel include awareness, interest, consideration, and action.
Let's delve deeper into each stage of the conversion funnel:
1. Awareness
In the awareness stage, potential customers become aware of your brand, product, or service. This can happen through various channels such as social media, search engines, online advertisements, or word-of-mouth referrals. At this stage, it is crucial to create compelling and engaging content that grabs the attention of your target audience.
For example, you could use eye-catching visuals, informative blog posts, or captivating videos to pique the interest of potential customers and make them aware of your offerings.
2. Interest
Once potential customers are aware of your brand, they move into the interest stage. Here, they show a genuine interest in what you have to offer and start exploring your products or services in more detail. They may visit your website, read product descriptions, compare prices, or seek customer reviews.
During this stage, it is essential to provide valuable and relevant information to keep potential customers engaged. You can offer detailed product specifications, customer testimonials, or even free trials to showcase the value and benefits of your offerings.
3. Consideration
In the consideration stage, potential customers are actively evaluating your offerings and comparing them with competitors. They may be weighing the pros and cons, assessing the value for money, or seeking additional information to make an informed decision.
At this stage, it is crucial to address any concerns or objections potential customers may have. You can provide detailed product comparisons, offer personalized recommendations, or showcase case studies that highlight successful outcomes for previous customers.
4. Action
The final stage of the conversion funnel is action. This is where potential customers make a purchase or complete the desired action, such as filling out a form or subscribing to a newsletter. It is the ultimate goal of the conversion funnel.
To encourage potential customers to take action, you can offer incentives such as limited-time discounts, free shipping, or a money-back guarantee. Additionally, optimizing the user experience, simplifying the checkout process, and providing multiple payment options can help reduce friction and increase conversion rates.
On the other hand, a conversion path describes the specific route a prospect takes to complete a conversion. It refers to the series of steps or touchpoints a user experiences before converting. This path can vary depending on the marketing strategy, channels utilized, and overall user experience. Unlike the conversion funnel, which focuses on the overall journey, the conversion path zooms in on the individual steps taken by a specific user.
Let's explore the components of a conversion path:
1. Initial Touchpoint
The conversion path begins with the initial touchpoint, where a user first interacts with your brand or marketing message. This could be through a social media post, a search engine result, an email, or a display advertisement. The goal of the initial touchpoint is to capture the user's attention and spark their interest.
2. Engagement
After the initial touchpoint, the user enters the engagement phase. This is where they actively engage with your content, website, or marketing materials. They may click on a link, watch a video, read a blog post, or explore product pages. The goal of this phase is to keep the user interested and encourage them to move further along the conversion path.
3. Conversion Trigger
The conversion trigger is the point at which the user decides to take action and convert. This could be triggered by a compelling offer, a persuasive call-to-action, or a sense of urgency. The conversion trigger is a critical moment in the conversion path, as it determines whether the user will proceed to the next step or abandon the process.
4. Conversion Completion
The final step in the conversion path is the conversion completion. This is where the user successfully completes the desired action, such as making a purchase, submitting a form, or signing up for a service. It is the ultimate goal of the conversion path and signifies a successful conversion.
By understanding and optimizing the conversion funnel and conversion path, businesses can effectively guide potential customers through the journey from awareness to action, ultimately increasing conversions and driving growth.
What's the difference between a Conversion Funnel and a Conversion Path?
Now that we have defined conversion funnels and conversion paths individually, let's delve into the key differences between the two:
Conversion funnels provide a high-level overview of the customer journey, while conversion paths offer a more granular view of the steps taken by an individual user.
Conversion funnels focus on the stages of the buyer's journey, from awareness to action, whereas conversion paths emphasize the touchpoints and interactions within each stage.
Conversion funnels are ideal for analyzing overall marketing performance and identifying bottlenecks, while conversion paths are useful for tracking and optimizing specific user interactions.
Examples of the Difference between a Conversion Funnel and a Conversion Path
2.1 - Example in a Startup Context
Imagine a startup company that offers a digital product. The conversion funnel would illustrate the broad stages of awareness, interest, consideration, and action that potential customers go through from their first encounter with the brand to making a purchase. In contrast, a conversion path within the funnel might indicate the specific touchpoints, such as visiting the website, signing up for a newsletter, and finally, clicking on a promotional email leading to a purchase.
2.2 - Example in a Consulting Context
In the consulting industry, a conversion funnel would outline the different stages a lead goes through, including initial research, free consultation request, further discussion, and signing a contract. Within this funnel, a conversion path could demonstrate the steps a lead took from discovering the consulting firm's website through a web search, downloading a whitepaper, attending a webinar, and finally, scheduling a consultation call.
2.3 - Example in a Digital Marketing Agency Context
For a digital marketing agency, the conversion funnel may depict the stages from awareness to action, including lead generation, nurturing, proposal submission, and contract signing. Within this funnel, a conversion path might reveal the specific touchpoints, such as clicking on a social media ad, filling out a contact form, attending a webinar, participating in a strategy session, and ultimately becoming a client.
2.4 - Example with Analogies
One way to understand the difference between a conversion funnel and a conversion path is through analogies. Think of a conversion funnel as a roadmap showcasing the main highways and landmarks along a journey, while a conversion path is like selecting the specific streets, turns, and intersections taken to reach a destination. Both provide valuable insights, but they focus on different levels of analysis and detail.
In conclusion, while conversion funnels and conversion paths are closely related, they serve different purposes in the realm of digital marketing. Understanding the distinction between them is essential for effectively analyzing marketing efforts, optimizing user experiences, and driving conversions. So, the next time you hear these terms being used, you can confidently differentiate between a conversion funnel and a conversion path.