
Decision criteria are essential factors that individuals or organizations consider when making a decision. They serve as the basis for evaluating different options and ultimately choosing the best course of action. In this article, we will delve into the definition of decision criteria, explore their advantages and disadvantages, and provide practical examples in various contexts, such as startups, consulting, and digital marketing agencies. We will also utilize analogies to help illustrate the concept further.
1. What are Decision Criteria?
Decision criteria encompass the specific factors that individuals or organizations prioritize when making a decision. These factors can include financial considerations, strategic objectives, customer preferences, technological feasibility, and many other relevant aspects. By establishing decision criteria, individuals or organizations can systematically evaluate different options and determine the best course of action.
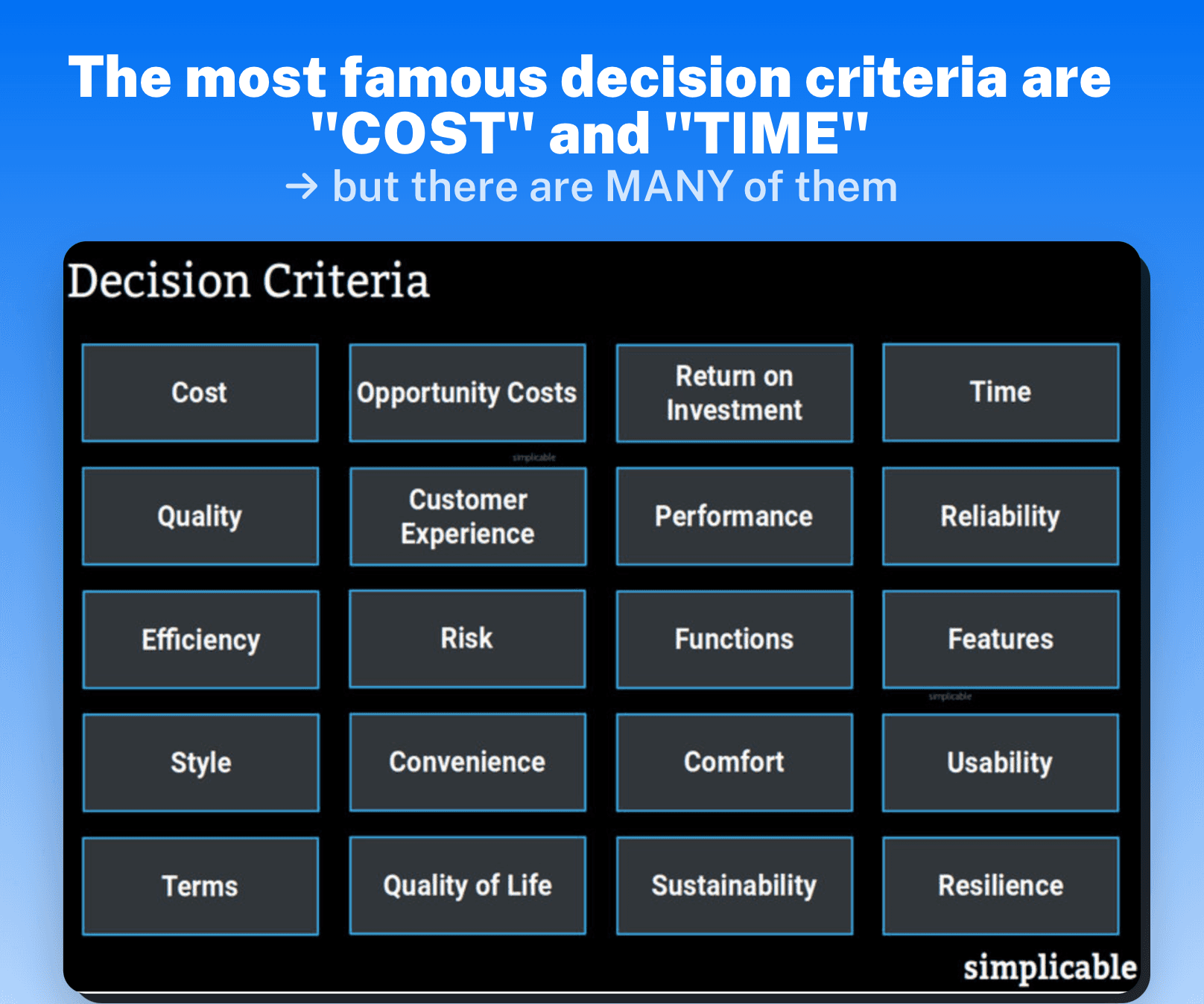
When it comes to decision-making, having clear and well-defined criteria is crucial. Decision criteria serve as a set of guidelines or standards that help individuals or organizations assess and compare different alternatives. These criteria can be quantitative or qualitative, depending on the nature of the decision and the available information.
1.1 Definition of Decision Criteria
Decision criteria refers to the specific standards or benchmarks used to assess different alternatives during a decision-making process. These criteria can be quantitative or qualitative and are often tailored to the specific context or goals of the decision-making process.
Quantitative decision criteria involve measurable factors that can be assigned numerical values. For example, in a financial decision, criteria such as return on investment (ROI), net present value (NPV), or payback period may be used. These criteria provide a clear and objective basis for evaluating options.
On the other hand, qualitative decision criteria involve subjective factors that are difficult to quantify but still play a significant role in the decision-making process. These criteria can include factors such as brand reputation, customer satisfaction, or ethical considerations. While they may not have precise numerical values, they are essential for capturing the intangible aspects that influence decision outcomes.
1.2 Advantages of Decision Criteria
Using decision criteria provides several benefits. Firstly, decision criteria help ensure that all relevant aspects are taken into account, leading to more comprehensive and informed decisions. By considering a range of factors, decision-makers can avoid overlooking critical aspects that could impact the success of the chosen option.

Secondly, decision criteria enable individuals or organizations to compare and prioritize different options based on their importance. By assigning weights or rankings to each criterion, decision-makers can objectively assess the pros and cons of each alternative. This allows for a more structured decision-making process and reduces the likelihood of relying on subjective judgments solely.
Lastly, decision criteria facilitate stakeholder collaboration and transparency as they provide a clear framework for evaluating options and aligning diverse perspectives. When decision criteria are well-defined and communicated, stakeholders can understand the rationale behind the chosen option and feel more engaged in the decision-making process.

1.3 Disadvantages of Decision Criteria
While decision criteria offer significant advantages, they are not without their limitations. One potential disadvantage is that decision criteria can oversimplify complex problems or situations. By focusing on specific factors, decision criteria may overlook critical nuances or underlying complexities that could impact the final decision. It is important for decision-makers to be aware of this limitation and consider additional information or expert opinions to supplement the criteria.
Additionally, decision criteria can be influenced by biases or limited perspectives, potentially leading to suboptimal outcomes. For example, if decision criteria heavily prioritize short-term financial gains, long-term sustainability or ethical considerations may be overlooked. To mitigate this risk, decision-makers should strive for a diverse and inclusive decision-making process that incorporates a wide range of perspectives and expertise.

In conclusion, decision criteria play a vital role in the decision-making process. They provide a structured framework for evaluating alternatives and help ensure that all relevant aspects are considered. However, decision criteria should be used judiciously, taking into account the limitations and potential biases they may introduce. By combining decision criteria with broader considerations and expert insights, individuals and organizations can make more informed and effective decisions.
2. Examples of Decision Criteria
Examining practical examples will further illuminate the concept of decision criteria. Let's explore how decision criteria can be applied in different contexts:
2.1 Example in a Startup Context
In a startup setting, decision criteria could include factors such as market potential, cost-effectiveness, scalability, and alignment with the company's vision and mission. By prioritizing these criteria, startup founders can evaluate potential business opportunities and make data-driven decisions that maximize chances of success.
For example, let's consider a tech startup that is developing a new mobile app. The decision criteria for this startup could involve analyzing the size of the target market, assessing the potential demand for the app, and evaluating the competition in the app market. Additionally, the startup may consider the cost-effectiveness of developing and maintaining the app, as well as its scalability potential in terms of user growth and revenue generation.
By carefully considering these decision criteria, the startup can make informed choices about whether to proceed with the app development, how to allocate resources, and how to position the app in the market.
2.2 Example in a Consulting Context
When working on a consulting project, decision criteria might involve client requirements, industry best practices, profitability, and long-term sustainability. By utilizing these criteria, consultants can assess alternative solutions and recommend the most suitable strategy to address the client's challenges and achieve their goals.
For instance, let's imagine a consulting firm that is tasked with helping a manufacturing company optimize its production processes. The decision criteria in this context could include analyzing the client's specific requirements, benchmarking against industry best practices, evaluating the potential profitability of proposed solutions, and considering the long-term sustainability of the implemented changes.
By carefully evaluating these decision criteria, the consulting firm can provide the client with a well-informed recommendation on how to streamline their production processes, improve efficiency, and ultimately achieve their desired business outcomes.
2.3 Example in a Digital Marketing Agency Context
In the context of a digital marketing agency, decision criteria could include factors such as target audience reach, cost per acquisition, return on investment, and campaign performance metrics. By incorporating these criteria, digital marketers can make data-informed decisions on the optimal marketing channels, strategies, and campaigns to maximize client's online presence and achieve desired business outcomes.
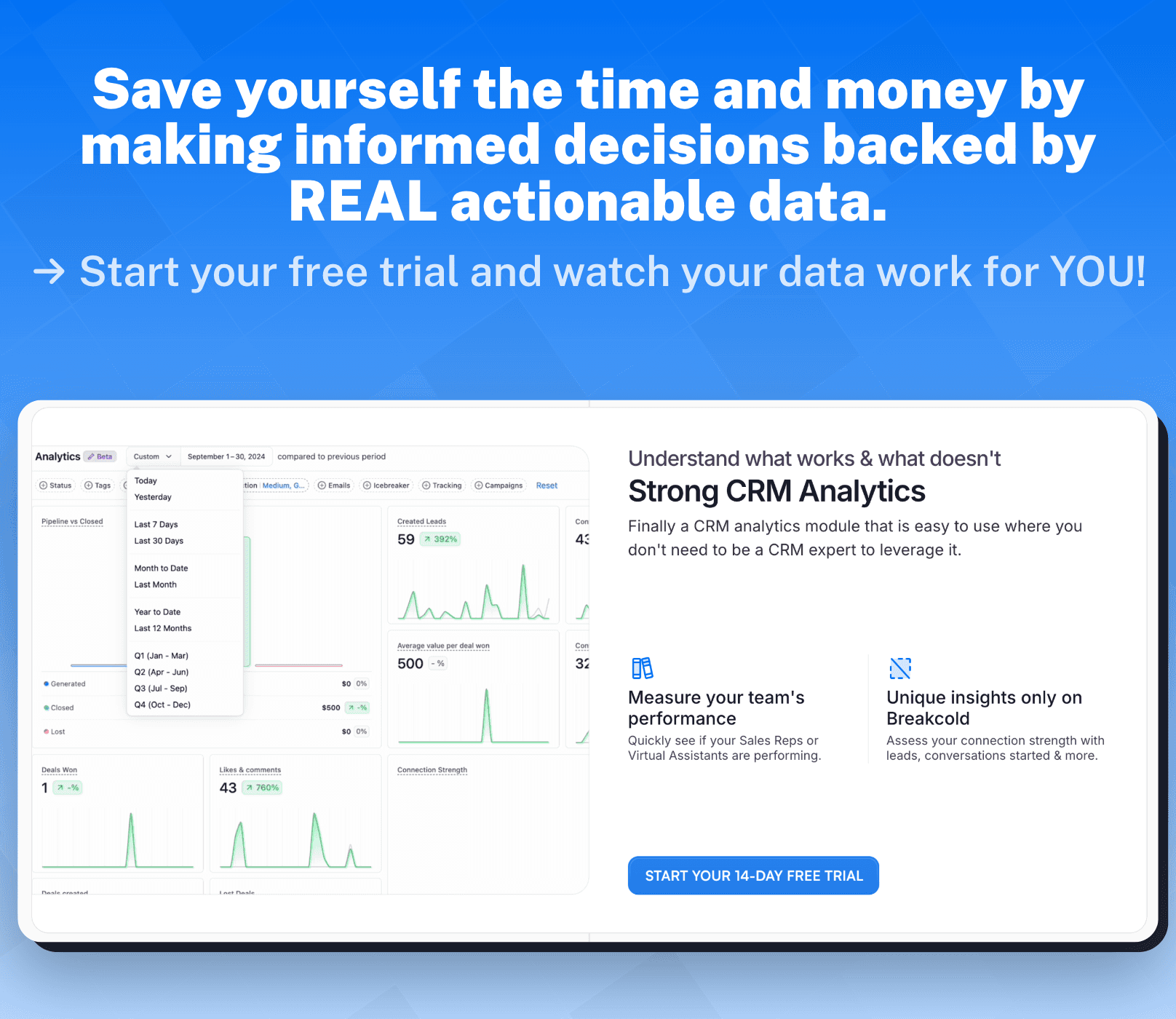
For example, let's consider a digital marketing agency that is working with an e-commerce client to increase their online sales. The decision criteria for this agency could involve analyzing the potential reach of different marketing channels, calculating the cost per acquisition for each channel, evaluating the expected return on investment for various marketing strategies, and monitoring campaign performance metrics such as click-through rates and conversion rates.
By carefully considering these decision criteria, the digital marketing agency can develop a tailored marketing plan that focuses on the most effective channels, strategies, and campaigns to drive targeted traffic to the client's website, increase conversions, and ultimately boost online sales.
2.4 Example with Analogies
To grasp the concept of decision criteria further, let's consider an analogy. Imagine you are choosing a holiday destination. The decision criteria might encompass factors such as travel costs, weather preferences, available activities, and cultural experiences. By evaluating these criteria, you can prioritize destinations that align with your preferences and make an informed decision on the best holiday spot.
For instance, let's say you are planning a vacation and have several potential destinations in mind. The decision criteria you might consider could include analyzing the cost of travel and accommodation, assessing the weather conditions and climate preferences, evaluating the availability of activities and attractions, and considering the cultural experiences each destination offers.
By carefully evaluating these decision criteria, you can narrow down your options and choose a holiday destination that suits your budget, weather preferences, desired activities, and cultural interests.
In conclusion, decision criteria play a crucial role in the decision-making process. They allow individuals or organizations to assess alternatives systematically, considering crucial factors and aligning decisions with their goals. While decision criteria have advantages such as comprehensiveness and clarity, it is important to be aware of their limitations and use them judiciously alongside broader considerations. By examining practical examples and analogies, we can better understand how decision criteria apply in various contexts and enhance our decision-making capabilities.











































































































































































































