
What is Pain Points Analysis? (Explained With Examples)
In today's competitive business landscape, understanding the needs and preferences of customers is crucial for success. To achieve this, companies often employ various methodologies to identify and address the pain points experienced by their target audience. In this article, we will explore the concept of Pain Points Analysis and illustrate its significance through real-life examples
What is Pain Points Analysis?
First and foremost, let's delve into the fundamentals of Pain Points Analysis. It is a systematic approach used by businesses to identify the specific challenges or frustrations faced by their customers or target market. By analyzing these pain points, companies gain valuable insights into the areas where their products or services can provide solutions and create a competitive advantage.
The picture below shows the result of our product analysis with my software: Breakcold CRM.

Pain Points Analysis involves a comprehensive examination of customer pain points, going beyond surface-level observations. It delves deep into the emotional and psychological factors influencing customer behavior. This analysis encompasses qualitative and quantitative research methods, such as surveys, interviews, and data analysis, to gather reliable information about customer pain points.
Implementing Pain Points Analysis offers numerous benefits to businesses. Firstly, it enhances customer satisfaction by identifying and addressing pain points. By improving customer experience, companies can build loyalty and boost overall satisfaction levels. Secondly, understanding customer needs and frustrations can drive innovation. Pain Points Analysis inspires innovative solutions, leading to the development of products or services that better cater to market demands. Thirdly, effectively addressing pain points delivers a competitive advantage. Companies that address pain points gain a competitive edge by differentiating themselves from rivals and surpassing customer expectations. Lastly, resolving pain points drives business growth. By addressing pain points, businesses can attract more customers, increase customer retention, and consequently drive revenue growth.
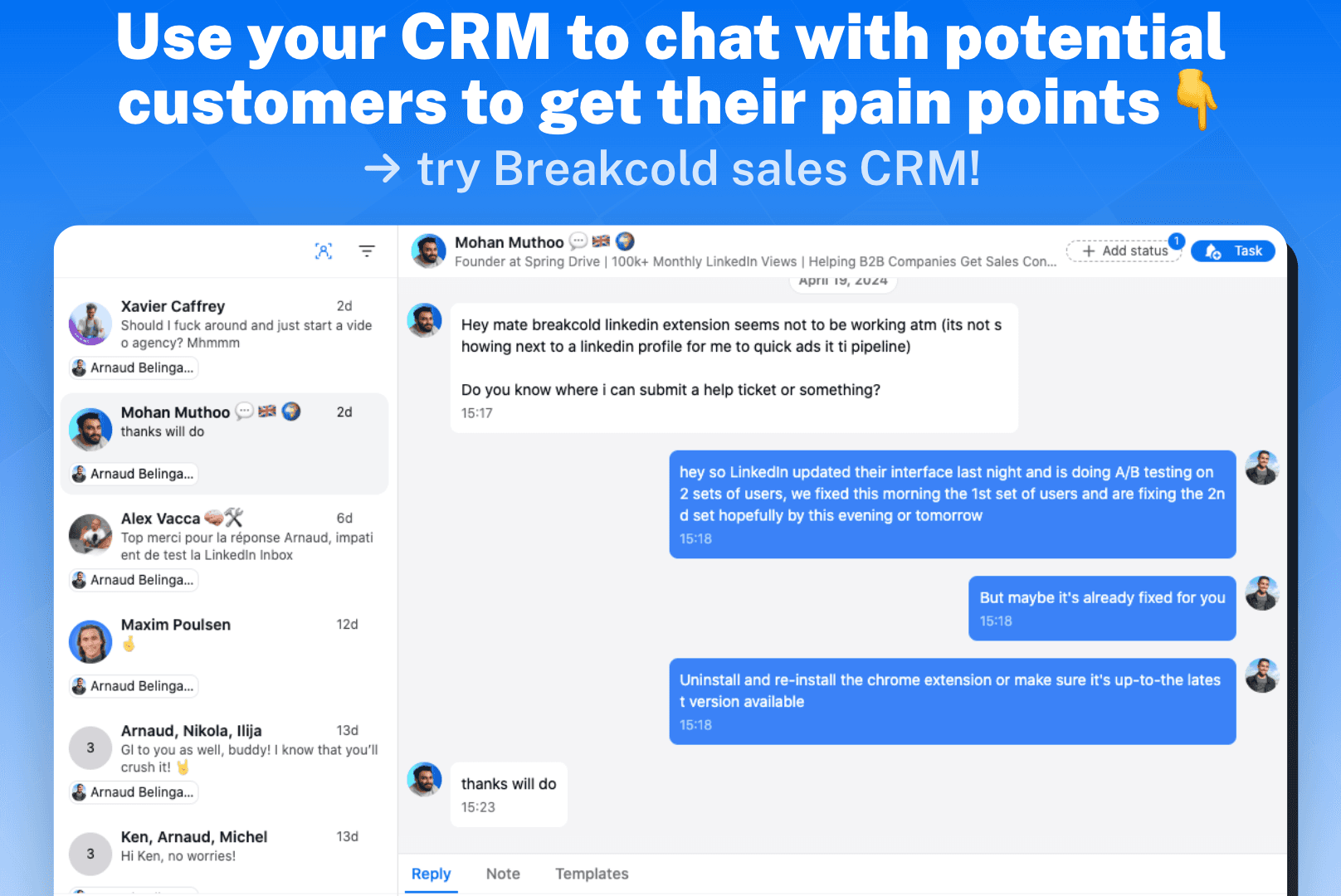
Despite its evident advantages, Pain Points Analysis also has potential limitations. Firstly, it involves interpreting qualitative data, which can introduce subjective biases and make it challenging to draw objective conclusions. Secondly, the accuracy and reliability of the collected data depend on the research methods and the willingness of customers to provide honest feedback. Thirdly, customer pain points can evolve over time, implying that continuous monitoring and adaptations are necessary to ensure relevance. Lastly, implementing a comprehensive Pain Points Analysis requires time, effort, and financial resources, especially when considering large-scale studies involving diverse customer segments.
Now that we have covered the foundational aspects of Pain Points Analysis, let's explore some illustrative examples that showcase its application and effectiveness in different contexts.
Examples of Pain Points Analysis
Example 1: In a Startup Context
Imagine a startup in the e-commerce industry that aims to disrupt the market with innovative features. Through Pain Points Analysis, the company identifies that potential customers are frustrated by the lengthy and complicated checkout process on existing platforms. Armed with this insight, the startup develops a streamlined and user-friendly checkout system, providing a seamless experience and addressing a widespread pain point.
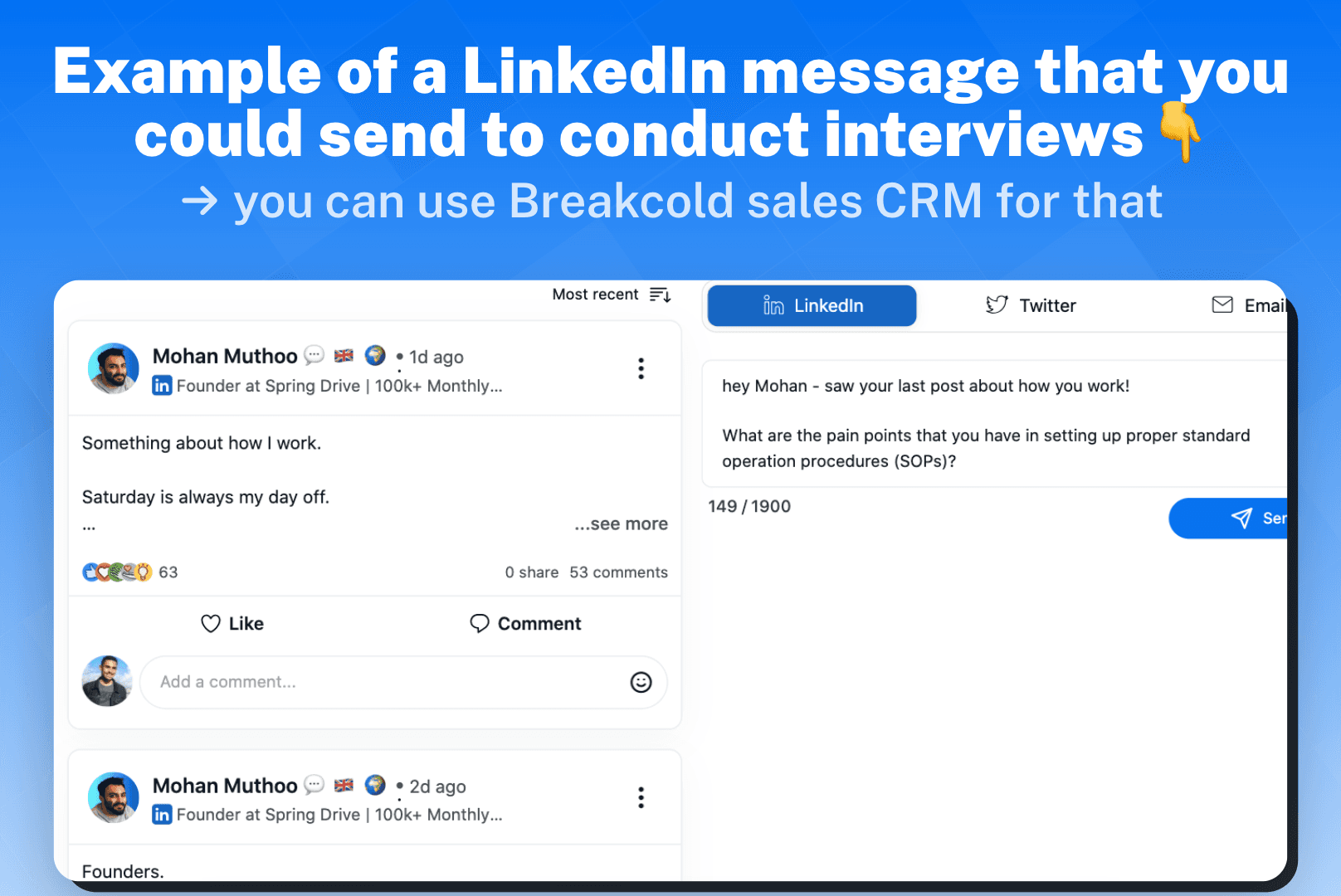
Example 2: In a Consulting Context
A consulting firm specializing in organizational change management conducts a Pain Points Analysis for its client, a struggling manufacturing company. Through interviews and data analysis, they identify that the lack of employee engagement and resistance to change are significant pain points. Leveraging this knowledge, the consulting firm designs a tailored change management program that effectively communicates the benefits of the proposed changes, fosters employee buy-in, and addresses the identified pain points head-on.
Example 3: In a Digital Marketing Agency Context
A digital marketing agency conducts Pain Points Analysis to understand the challenges faced by its clients in the realm of social media management. They discover that many clients struggle with creating engaging content consistently. Armed with this knowledge, the agency develops customized content creation frameworks and tools, allowing their clients to overcome the pain points and achieve better social media performance.
Example 4: With Analogies
Lastly, let's showcase an example that utilizes analogies to illustrate pain points. Consider a coffee shop that wants to attract customers during off-peak hours. By analyzing customer feedback, the coffee shop discovers that potential customers perceive crowded seating areas and long wait times as significant pain points. To address this, the coffee shop redesigns its seating layout, creates designated pickup areas, and implements an efficient ordering system akin to a well-organized airport terminal - seamlessly transforming the previously frustrating experience into a smooth and enjoyable one.
By examining these real-life examples, we can observe how various businesses successfully leverage Pain Points Analysis to identify crucial pain points and design effective solutions that significantly enhance customer satisfaction and organizational success.
In conclusion, Pain Points Analysis serves as a powerful tool for businesses to gain actionable insights into customer challenges and unfulfilled needs. By understanding and rectifying these pain points, companies can ensure customer satisfaction, foster innovation, and ultimately achieve sustainable growth. Embracing this methodology enables businesses to empathize with their customers, tailor their offerings, and distinguish themselves in today's fiercely competitive market.











































































































































































































