
What is Data Segmentation? (Explained With Examples)
Data segmentation is a crucial concept in the world of data analysis and marketing. It refers to the process of dividing a large dataset into smaller, more manageable subsets based on specific criteria or characteristics. By segmenting data, organizations can gain valuable insights and tailor their strategies to target specific groups of customers or users. In this article, we will explore what data segmentation is, its definition, advantages, and disadvantages, as well as provide examples of how it can be applied in various contexts
1°) What is Data Segmentation?
Data segmentation can be defined as the practice of categorizing data based on specific attributes or factors. This process allows organizations to group similar data together, making it easier to analyze and derive meaningful insights. By segmenting data, businesses can better understand their target audience and make informed decisions to enhance their operations and marketing efforts.
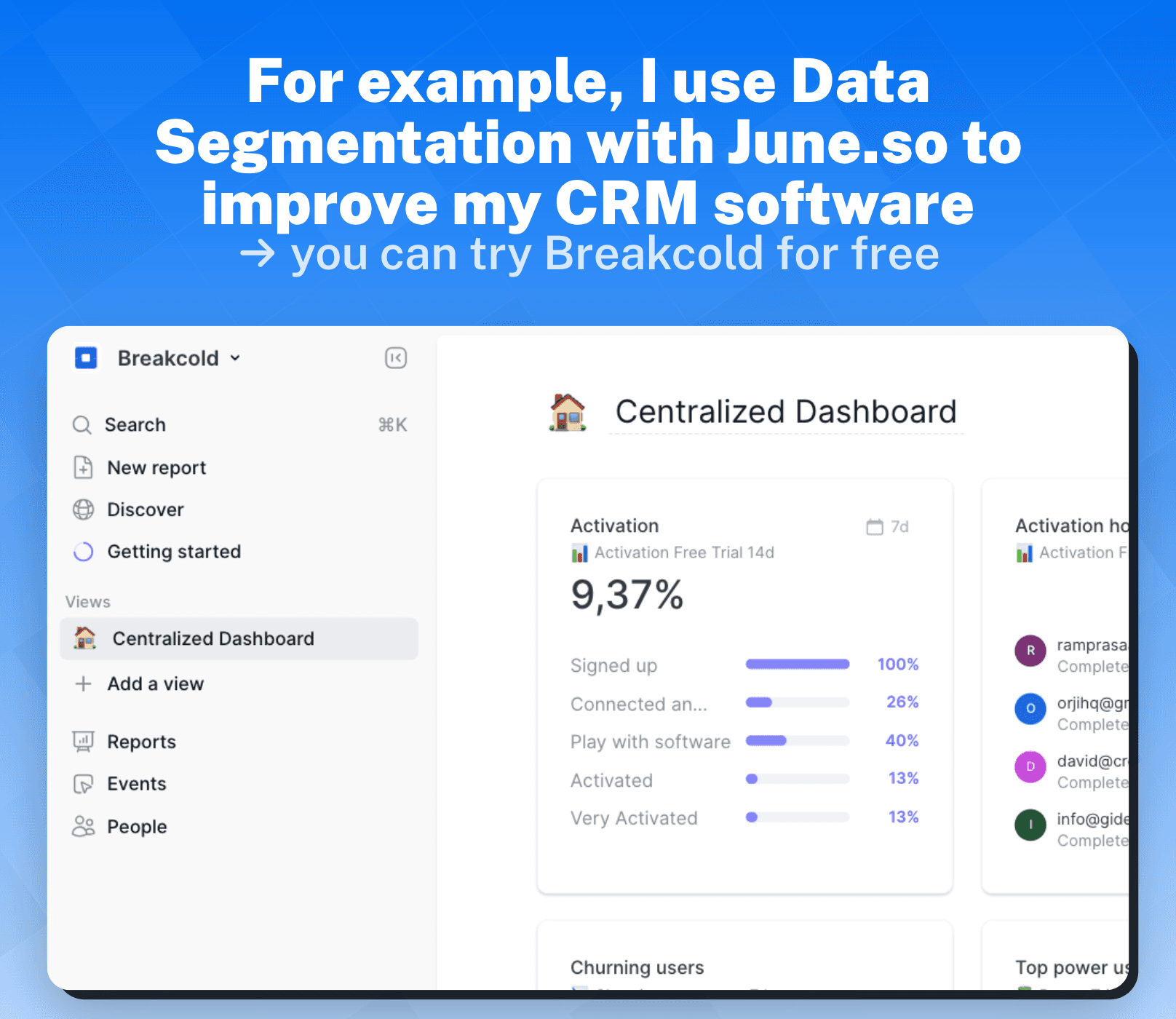
1.1 - Definition of Data Segmentation
When we talk about data segmentation, we are referring to the process of dividing a dataset into smaller subsets based on specific variables or criteria. These variables can include demographic information such as age, gender, location, or behavioral data like purchase history, website interactions, or social media engagement. The goal is to identify distinct groups within the dataset that share similar attributes and behaviors.
For example, an e-commerce company might segment its customer data based on past purchase behavior. By analyzing the data, they could identify different groups of customers, such as frequent buyers, occasional shoppers, or one-time purchasers. This segmentation allows them to tailor their marketing messages and promotions to each group, increasing the chances of attracting and retaining customers.

1.2 - Advantages of Data Segmentation
Data segmentation offers several advantages for businesses and marketers:
Targeted Marketing: By segmenting data, organizations can create targeted marketing campaigns that are more likely to resonate with specific customer groups. This can lead to higher engagement, conversion rates, and ROI.
Personalization: Segmenting data enables businesses to personalize their communication and offerings based on the preferences and needs of different customer segments. Personalized experiences can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Improved Decision Making: By analyzing segmented data, organizations can gain insights into the behavior and preferences of different customer segments. This information can inform better decision-making, such as product development, pricing strategies, or resource allocation.
Resource Optimization: By allocating resources based on specific customer segments, businesses can optimize their marketing budgets and efforts. Instead of targeting a broad audience, they can focus on segments that are more likely to convert or engage with their offerings.
Targeted marketing is one of the key advantages of data segmentation. By understanding the specific needs and preferences of different customer segments, businesses can create customized marketing campaigns that are more likely to resonate with their target audience. For example, a clothing retailer can segment their customer data based on gender and age group. This segmentation allows them to create targeted advertisements and promotions that cater to the unique fashion preferences of each segment. As a result, they can increase the effectiveness of their marketing efforts and drive higher conversion rates.
Another advantage of data segmentation is the ability to personalize communication and offerings. By understanding the preferences and needs of different customer segments, businesses can tailor their messages and product recommendations to each group. For instance, an online streaming service can segment its user data based on genre preferences. This segmentation allows them to provide personalized recommendations to each user, suggesting movies or TV shows that align with their interests. This level of personalization enhances the user experience and increases customer satisfaction and loyalty.
1.3 - Disadvantages of Data Segmentation
While data segmentation offers many benefits, there are also some potential drawbacks to consider:
Complexity: Segmenting data can be complex, requiring careful planning and analysis. Organizations need to ensure they have the necessary resources and expertise to carry out effective segmentation.
Data Quality: Data segmentation relies on accurate and reliable data. If the underlying data is incomplete, outdated, or incorrect, the resulting segmentation may not yield meaningful insights.
Overgeneralization: It's essential to strike the right balance when segmenting data. Over-segmentation can result in too many small, niche segments that may not be practical or cost-effective to target individually.
Privacy Concerns: Segmenting data raises privacy concerns, as it involves collecting and storing personal information. Organizations must comply with relevant data protection laws and ensure data security to protect the privacy of their customers.
One potential disadvantage of data segmentation is the complexity involved in the process. Effective segmentation requires careful planning, analysis, and the use of appropriate tools and techniques. Organizations need to invest in resources and expertise to carry out segmentation effectively. This can include hiring data analysts or investing in data segmentation software.
Data quality is another potential drawback of data segmentation. To obtain meaningful insights from segmented data, it is crucial to have accurate and reliable data. If the underlying data is incomplete, outdated, or incorrect, the resulting segmentation may not accurately represent the target audience or provide valuable insights. Therefore, organizations need to ensure data quality by regularly updating and validating their data sources.
Overgeneralization is a common pitfall in data segmentation. While segmenting data can provide valuable insights, it is essential to strike the right balance. Over-segmentation can result in too many small, niche segments that may not be practical or cost-effective to target individually. Organizations need to consider the size and potential value of each segment before deciding on their marketing strategies.
Lastly, privacy concerns are a significant consideration when it comes to data segmentation. Segmenting data involves collecting and storing personal information, which raises privacy concerns. Organizations must comply with relevant data protection laws and regulations to ensure the privacy and security of their customers' data. This includes implementing robust data security measures and obtaining proper consent from individuals before collecting and using their data for segmentation purposes.
2°) Examples of Data Segmentation
Let's explore practical examples of how data segmentation can be applied in different contexts:
2.1 - Example in a Startup Context
In a startup context, data segmentation can help identify the most promising customer segments for a new product or service. By analyzing user demographics, preferences, and behavior, startups can target their marketing efforts to reach the most receptive audience.
For instance, a health tech startup developing a fitness app might segment its user data into groups based on age, fitness goals, and activity levels. This segmentation could enable them to create personalized workout plans or offer targeted nutrition advice, increasing user engagement and satisfaction.
2.2 - Example in a Consulting Context
Data segmentation is also valuable in a consulting context, particularly when conducting market research or advising clients on business strategies. By segmenting market data, consultants can provide more tailored insights and recommendations to their clients.
For example, a management consulting firm analyzing the food delivery market might segment the data based on geographical regions, customer preferences, and market saturation. This segmentation could help them identify untapped market opportunities or advise their clients on how to differentiate their offerings based on specific customer segments.
2.3 - Example in a Digital Marketing Agency Context
In the digital marketing world, data segmentation is an indispensable tool for optimizing advertising campaigns and improving targeting. By segmenting customer data, digital marketing agencies can create highly targeted ads that resonate with specific customer segments, leading to higher conversion rates.
For instance, a digital marketing agency helping a client promote a luxury travel service could segment the target audience based on income levels, travel preferences, and previous travel history. This segmentation would allow the agency to craft personalized ads that highlight exclusive experiences or tailored offers, maximizing the chances of attracting high-end customers.
2.4 - Example with Analogies
To illustrate the concept of data segmentation, let's use two analogies:
Imagine you have a large wardrobe filled with various types of clothing. Instead of trying to organize everything at once, you decide to segment your wardrobe into specific sections – one for formal wear, another for casual attire, and a third for sports-related clothing. This segmentation makes it easier for you to find the right outfit for different occasions without wasting time searching through the entire wardrobe.
Consider a library with thousands of books on various subjects. To make it easier for readers to find books of interest, the library uses a system of categorization and segmentation, such as separating books into different sections based on genres or topics. This way, readers can navigate the library efficiently and locate books that align with their specific interests.
In both of these examples, segmentation simplifies organization and improves the overall efficiency and effectiveness of finding what you need. Similarly, data segmentation helps businesses make sense of complex datasets by breaking them down into meaningful subsets for analysis and decision-making.
In conclusion, data segmentation is a powerful technique that enables organizations to gain valuable insights and cater to specific customer groups or audiences. By defining data segmentation, understanding its advantages and disadvantages, and exploring real-world examples, businesses can leverage this practice to enhance their strategies, improve targeting, and drive success in today's data-driven world.











































































































































































































